12 common risks of cloud computing+ How to avoid them.

What are the 12 common risks of Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a distributing computer service such as software, analytics, databases, servers, storage, and intelligence to provide quicker innovation and adaptable resources. Data and the program can be remotely stored and instantly accessed via the internet using a web browser. However, using cloud apps often results in getting the risks of cloud computing.
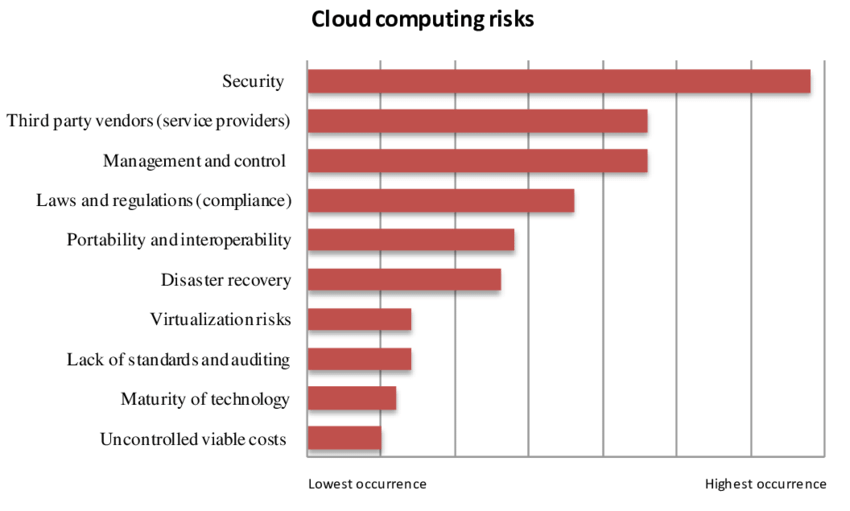
Photo Credits: Research Gate
What are the basic models for Cloud Computing Services?
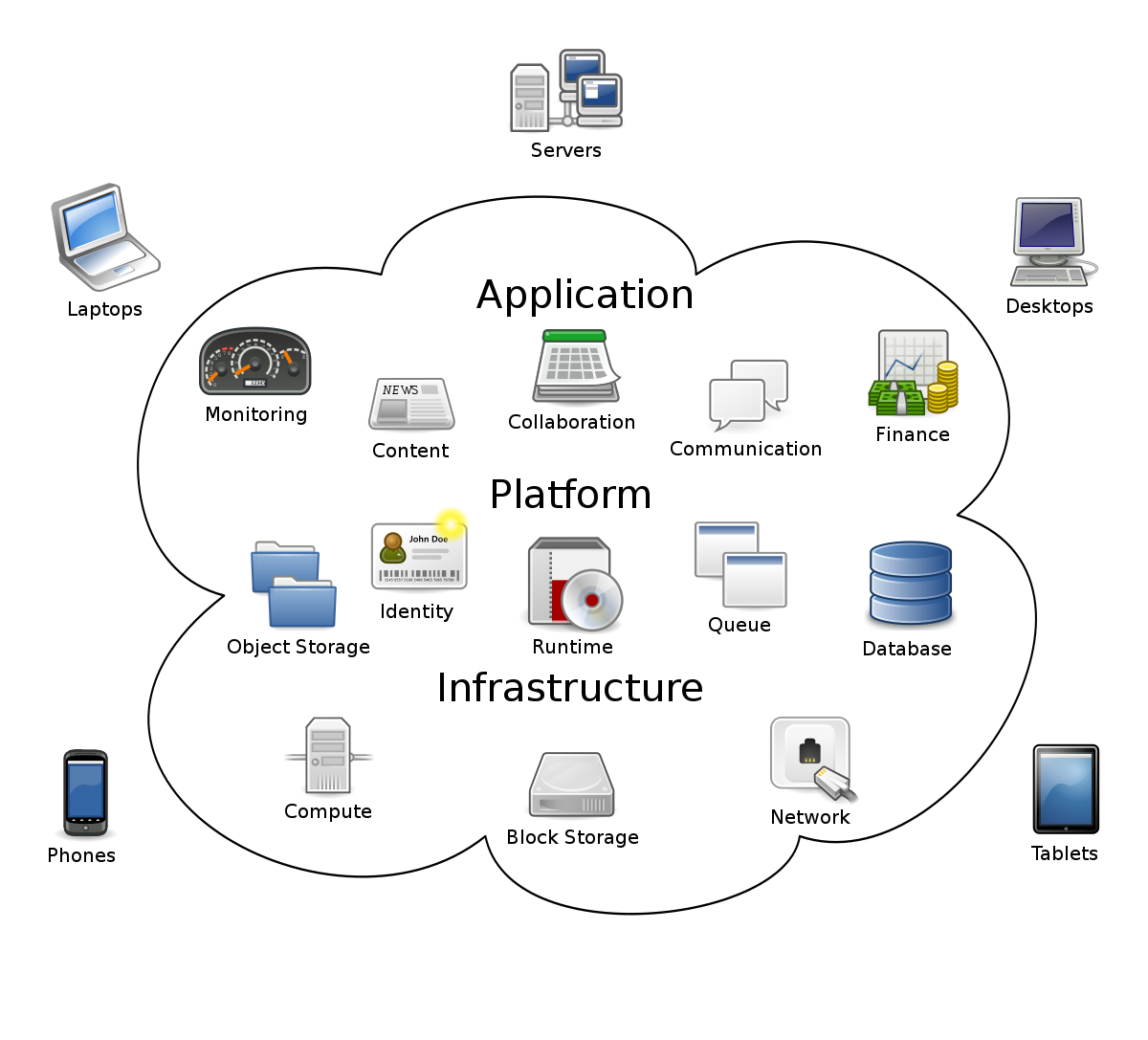
While some vital features of Cloud Computing Services include widespread network connectivity, virtualized resources, quick adaptability, and timely deliveries, the basic models for cloud computing are divided into two parts:
- Service Models: These are further divided into SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS
- Deployment Models include hybrid and public Cloud and community and private Cloud.
Cloud computing has many benefits, but it also has drawbacks. If you’re thinking about shifting your company to the Cloud, you should know the major risks of cloud computing.
What are the 12 Common Risks of Cloud Computing?
1 Reduced Visibility and Control:
Organizations need to critically analyze application data without utilizing network-based surveillance, as they might lose some of their visibility in network operations while shifting assets to the Cloud. In addition, the responsibility range switch may shift depending on the service model implemented. Without using network-based monitoring and logging, enterprises can monitor their network infrastructure.
2 Compliance:
Compliance refers to the possibility of provider-level consent diverging from the user-applied regulations. Most businesses nowadays operate with some regulatory system over their data. These regulations require companies to understand where their data is, who can access it, and how it is protected. Suppose suitable security measures are not there to filter out various people. In that case, nearly everyone can readily access the data because cloud services often offer a broad-scale user access panel.
3 Malware:
Up to 90% of organizations expose themselves to cyber risks when moving essential, sensitive data to a cloud system. The organization’s data may be accessible to an attacker who gets a CSP administrator’s cloud credentials, allowing them to steal or damage the agency’s data. In addition, any sensitive file or media content can contain malware, which can be published on social media sites. As cyber criminals develop new ways of surpassing online security daily, organizations generate a way to make their data more secure.
4 Data Deletion:
Over 60% of sites believe data deletion is their biggest security concern in a multitenancy environment. Threats related to data deletion exist because the user has less insight into where their data is being held in the Cloud. In addition, the providers use varying deletion processes; thus, organizations cannot confirm that they safely erased the data and if any residual data may still be available to attackers. This risk grows as companies increasingly use CSP services.

5 Vulnerability of Credentials:
An attacker steals a user’s CSP credentials, giving them access to a wide range of private data. Additionally, the attacker gains access to the CSP’s services and uses them to add additional information, targeting administrative users using the same CSP. Therefore, not only will the end-user lose its data, but it also causes damage to cloud credibility.
6 IT Staff’s Due Diligence:
To ensure that your team has a solid grasp of the work required to shift to the Cloud successfully, it is crucial to do extensive due diligence before collaborating with a cloud service provider. Besides the fact that key management and encryption services are complex and challenging, tools available to log cloud services often vary across CSPs. As a result, an agency’s Cloud and on-premises deployments may be more susceptible to security flaws.
7 Accidental Loss Of Data:
Data loss sometimes occurs despite malware and hacker attacks. For example, users often lose their encryption keys and settings. Here, the Cloud deletes that customer’s data if the user doesn’t update data and privacy settings on time.
8 Failure in the CSP Supply Chain:
If the CSP does not enforce compliance and subject the third party to its requirements, the threat to an agency’s information may escalate. If the CSP moves its infrastructure, operations, or maintenance, the third party concerned may not meet its requirements. This should be a noble cause of concern for the agency because this puts their data and information stored on the Cloud in damaging hands. The application or site and another third party must have a common ground on the Cloud.
9 Risks from incomplete separation amongst users
CSP’s platform, infrastructure, or application support tenants. The likelihood of an attacker accessing another user’s account increases if there is an incomplete separation between the co-users. If the separation measures are ineffective, multi-tenancy broadens the attack surface and increases the risk of data leakage.
10 Self-Service Makes Unauthorized Use Simple
Using a CSP’s new services is convenient for the Cloud of ITS departments. However, this self-service cloud computing results in unauthorized users. Services provided or used without ITS authorization put the application at risk. Since the corporation cannot defend resources, it is unaware of and could increase malware infections or data exfiltration.
11 APIs:
Customers can control and engage with cloud services via a set of application programming interfaces (APIs) that CSPs expose. Similar vulnerabilities exist in these APIs as with an operating system API. However, they exploit more as they are vastly exposed to the internet. Any API weaknesses could lead to successful attacks, compromising the cloud data of the website.
12 Internet-a necessity:
Cloud computing only functions when the internet is available. Mostly, companies use cloud computing utterly for their data storage. Therefore, they may lose their secure data for a short period if the internet is unavailable. In addition, including any other IT system, the Cloud is susceptible to technical issues like reboots, network disruptions, and downtime. These occurrences can cripple business procedures and cause financial harm.
How can you overcome the risks of cloud computing?
One method of examining the risks of cloud computing is to carry out cyber security risk assessments. To guarantee the integrity of your data, it is crucial to be vigilant about CSPs and how they operate. Poor infrastructure is a common issue. You can remove it by using Cloud Hybrid, where network operators will manage the change and significantly lessen the time and expense of your firm. You can also save yourself from the risks of cloud computing by enabling multi-factor authentication.
Related Resources:
Read more: What is a cloud ERP system?
AWS vs MS Azure vs Google Cloud: Overview, Pros and Cons

