SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS: What’s the Difference and How to Choose

The comparison and struggle in the top three cloud computing services, SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS, are intense and high nowadays. It is the practice of using the network, its on-demand availability of computer resources, particular data storage, and computer power.
SaaS, PaaS, and LaaS are three excellent cloud services. We are trying to help you understand the concept of these terms, and these are sometimes very hectic and tough tasks to know the difference between Saas vs PaaS vs IaaS. Let us take the overview of these three cloud computing services.
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS Overview
SaaS accounts for about 24 percent of all enterprises **up from 14% in 2016**. IaaS is flying and growing about 12 percent **up from 6%**. PaaS is nowadays a famous service, growing about 32 percent & probably grow 40 percent.
-SaaS ^Software-as-a-Service^
Allows programs to run automatically & is approachable via the Internet. So we don’t need to process from other services.
– PaaS ^Platform-as-a-Service^
Through PaaS, we can create applications in a short time. It manages and controls the service of the basic physical and structural facilities
-IaaS ^Infrastructure-as-a-Service^
It provides circumstances that are under the control & automated.
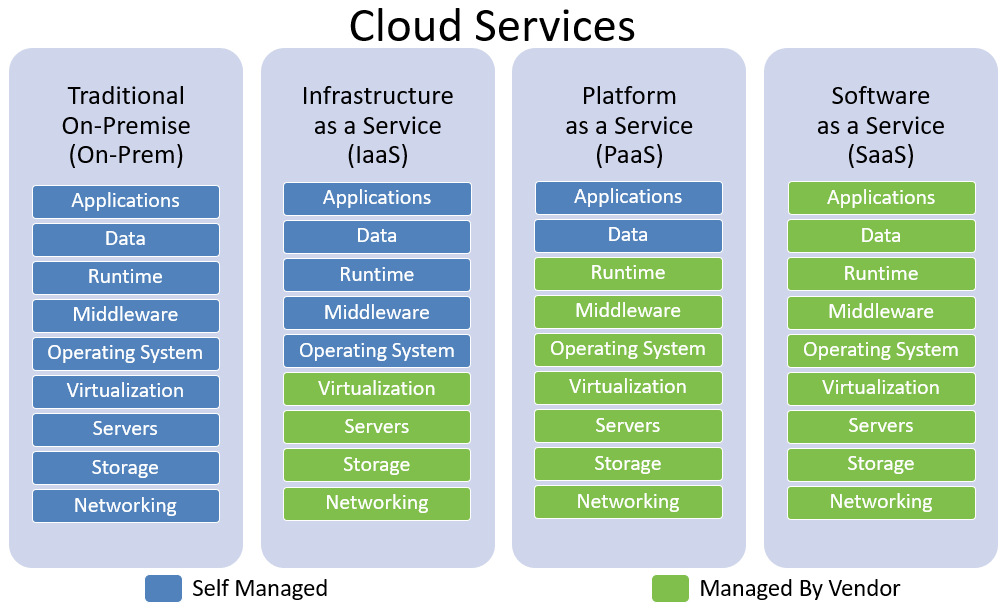
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS:
SaaS (Software as a service)
Software as a service (SaaS) is the software program distribution provider wherein a cloud company runs programs and permits them to be had to the end customers through the internet. In this provider, an impartial software program seller can settle a third-celebration cloud company to the host of the utility.
It works through the cloud transport model. A software provider will host the application and related data utilizing its servers, databases, networking & computing resources. This application will be approachable to any device with the help of a connection to the Internet. These applications are generally approachable via the Website browsers.
Vertical vs horizontal SaaS
Horizontal & vertical SaaS are the two unique cloud computing services models. Horizontal SaaS has a specialty of an expanded variety of clients, typically without regard to their industry. Flat SaaS’s famous examples are the Salesforce & HubSpot. While Vertical SaaS denotes the area of interest market focusing on a significantly narrower form of clients to satisfy and fulfill their precise demands
SaaS advantages
SaaS gets rid of the want for corporations to put in and run programs on their computer systems or their information centers. This gets rid of the fee of hardware acquisition, provisioning, and maintenance, in addition to software program licensing, setup, and help. Other blessings of the SaaS version include:
- Flexible payments. Clients join a SaaS offering rather than shopping software programs to put in or extra hardware to help it. Transitioning fees to habitual running fees lets many groups work out higher and more predictable budgeting. Users can also terminate SaaS services to forestall the customary fees.
- Scalable usage. Cloud offerings like SaaS provide extreme Vertical scalability, which offers clients the choice to get entry to extra or fewer offerings or capabilities on demand.
- Automatic updates. Rather than shopping for a new software program, clients can depend on a SaaS company to routinely carry out updates and patch management. This similarly reduces the load on in-residence IT staff.
- Accessibility and persistence. Since SaaS providers supply programs over the internet, customers can get entry to them from any internet-enabled tool and location.
- Customization. SaaS programs are regularly customizable and may be included with different enterprise programs, especially throughout programs from a not unusual place software program company.
SaaS challenges and risks
Additionally, SaaS poses a few capacity dangers and challenges, as groups should rely upon outdoor carriers to offer the software program and hold that software program up and running. Also helpful in tuning and documenting correct billing and facilitating a steady surrounding for the business’s information.
- Issues beyond client control: Issues arise while companies enjoy provider disruptions, impose undesirable adjustments to provide services, or enjoy a safety breach –All of that may have a profound effect on the customers’ capability to use the SaaS offering. To proactively mitigate the issues, customers need to understand their SaaS company’s SLA and make sure it’s far enforced.
- Customers lose management over versioning: If the company adopts a new edition of an application, it will roll out to all of its clients, irrespective of whether or not or now no longer or now not the consumer desires the greater modern version. This may also require the agency to offer more time and assets for training.
- Switching carriers difficulty: As with any cloud provider company, changing carriers may be complex. To transfer pages, clients should migrate very vast quantities of information. Furthermore, a few carriers use proprietary technology and information types, which could, in addition, complicate client information switch among distinct cloud companies. Vendor lock-in is when a client can’t, without difficulty, transition among provider companies because of those conditions.
- Security: Cloud safety is frequently noted as a significant assignment for SaaS applications.
SaaS examples: Big Commerce, Sales pressure, and Dropbox
PaaS (Platform as a service)
Platform as a service (PaaS) is a cloud computing service where 3rd -party providers provide the hardware and software instruments to users via the internet. Mostly, these are needed for the development of the application.
APPLICATIONS :
PaaS can be performed in 3 ways:
1-As a public cloud service from a provider, here the consumer controls software deployment with minimal configuration options, and the provider provides the networks and storage 2- private service behind a firewall three the last one is the software deployed on the public infrastructure
Common PaaS scenarios
Organizations usually use PaaS for those scenarios:
1. Development framework: PaaS gives a framework that developers can construct upon to develop or customize cloud-primarily based totally programs. Similar to the way you create an Excel macro, in PaaS, we could developers create programs using integrated software program components. Cloud capabilities consisting of scalability, high availability, and multi-tenant functionality are included, decreasing the quantity of coding that developers need to do.
2. Analytics or enterprise intelligence: Tools supplied as a service with PaaS permit businesses to research and mine their data, locating insights and styles and predicting effects to enhance forecasting, product layout decisions, funding returns, and different business decisions.
3. Additional services: PaaS carriers might also additionally provide different services that enhance applications, consisting of workflow, directory, security, and scheduling.
TYPES OF PaaS:
- Public PaaS is obtained from the service of software & is located in the cloud computing in between SaaS and IaaS
- A private PaaS can generally be downloaded & installed in a company’s on-premises or the public cloud. When the software is installed on one or more machines, private PaaS arranges the application and database elements.
- Hybrid PaaS is generally a deployment composed of a mix of public & private implementations.
- Communications PaaS is the cloud-based platform that makes developers add a feature in real-time communications.
- Mobile PaaS *PaaS* gives capabilities for developing mobile applications for designers and developers. Its theme recognized in 2014
- Open PaaS service doesn’t consist of hosting though it gives open-source software.
ADVANTAGE AND DISADVANTAGE
Advantages of PaaS
By handing over infrastructure as a provider, PaaS gives identical advantages to IaaS. But its extra features—middleware, development equipment, and different enterprise equipment—provide you with greater benefits:
- Cut coding time. PaaS development equipment can reduce the time it takes to code new apps with pre-coded application components built into the platform, inclusive of workflow, listing services, safety features, search, etc.
- Add development capabilities without which include a team of workers. Platform as a Service component can offer your development organization new abilities without your wanting to function team of workers having the favored abilities.
- Develop for a couple of platforms—such as mobile—more quickly. Some service carriers provide improvement alternatives for a couple of media, including computers, cell devices, and browsers making cross-platform apps faster and less complicated to develop.
- Use sophisticated equipment affordably. A pay-as-you-move version makes it feasible for people or businesses to apply sophisticated improvement software programs and enterprise intelligence and analytics equipment that they couldn’t have enough money to buy outright.
- Support geographically disbursed development groups. Because the development surroundings are accessed over the Internet, development groups can work collectively on initiatives even if group members are in far-off locations.
- Efficiently manipulate the software lifecycle. PaaS offers all the skills you want to assist the complete web application lifecycle: building, testing, deploying, managing, and updating in the identical incorporated surroundings.
PaaS Examples: AWS Elastic Beanstalk and Windows Azure.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS provides the services like networking and pay-as-you-go storage. It gives customers cloud-primarily based options to on-premise infrastructure so that agencies can hold away from the expense of the site resources, and its delivery is over the Internet.
Common IaaS Business Scenarios:
1. lift-and-shift migration: This is the quickest and least highly-priced approach to migrating a utility or workload to the cloud. Without refactoring your underlying architecture, you could boom the dimensions and overall performance, beautify the security, and decrease the expenses of walking a utility or workload.
2. Test and improvement: Your group can use speedy installation and dismantle check and improvement environments, bringing new packages to the marketplace faster. IaaS makes it brief and cost-effective to scale dev/check environments up and down.
3. Storage, backup, and restoration: Your corporation avoids the capital outlay for the garage and the complexity of garage control, which usually calls for a professional workforce to manipulate statistics and meet felony and compliance requirements. IaaS is beneficial for coping with an unpredictable call for progressively developing garage needs. It also can simplify the planning and management of backup and recovery systems.
4. Web apps: IaaS presents all of the infrastructures to help internet apps, consisting of a garage, internet and alertness servers, and networking resources. Your corporation can provide speedy install internet apps on IaaS and, without difficulty, scale infrastructure up and down while the call for the apps is unpredictable.
5. High-overall performance computing: High-overall performance computing on supercomputers, pc grids, or pc clusters allows resolve complicated issues regarding hundreds of thousands of variables or calculations. Examples encompass protein folding and earthquake simulations, weather and climate predictions, monetary modeling, and product layout evaluations
IaaS Advantage :
- Reduces capital fees and optimizes expenses: IaaS eliminates the cost of configuring and coping with a bodily data center, making it a fee-powerful preference for migrating to the cloud. The pay-as-you-cross subscription fashions utilized by IaaS companies assist you in lessening hardware expenses and renovation. Furthermore, it permits your IT group to recognition on medium commercial enterprises.
- Increases scale and overall performance of IT workloads: IaaS helps you scale globally and accommodate spikes in good resource demand. That way, you may supply IT sources to personnel from everywhere withinside the global quicker and decorate overall utility performance.
- Increases stability, reliability, and supportability: With IaaS, there is no want to hold and improve software programs and hardware or troubleshoot device problems. With the precise settlement in place, the carrier company assures that your infrastructure is dependable and meets carrier-stage agreements (SLAs).
- Improves commercial enterprise continuity and catastrophe healing: Helps to achieve excessive availability; commercial enterprise continuity and catastrophe healing are high priced. It calls for a great quantity of generation and staff. But with the proper SLA in place, IaaS enables to lessen this fee. Additionally, it allows you to get the right of entry to programs and statistics as regular all through a catastrophe or outage.
- Enhances security: With the appropriate provider agreement, a cloud carrier company can provide higher protection in your programs and statistics than the safety you will achieve in-house.
IaaS Examples: Backspace and Goggle Compute Engine
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS
Related Articles: Custom Software Development Trends in 2021.

