Whenever you search for enterprise resource planning (or ERP) systems various websites will present you with their own interpretations of what they think an ERP is. We’re not saying they’re wrong but every ERP differs from the other in some way. You will understand this as you reach the end of this blog.
We develop ERP systems to integrate them into your business model so the software manages all core operations of manufacturing, services, supply chain, and any other operations. Consequently, an ERP system is a software designed to integrate all of the business’s functions into one unified system.
Everyone is talking about ERP system nowadays. To understand how it can transform your business and increase your ROI, we will go deeper into what ERP systems actually are.
History of ERP Systems
To understand ERP systems, it is important that you know some history. You may have heard of the wide use of Inventory Management Systems in the past. They kept track of inventory, monitor status, and the balance of income. The concept of ERP systems was already in use under inventory management systems, even though it was coined in 1990. Back then, they were also called Manufacturing Resource Planning or MRP-II.
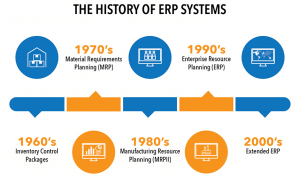
In 1990 however, when the term was coined it clearly differentiated MRP only systems for ERP systems on the basis of the extra operations like accounting, human resource management, etc. that they could manage.
In the 2000-2005 era these systems were slowly moving to the cloud. Developers started to make “Internet Enabled” solutions rather than the old on-premise client-server models. Thus began the globalization of ERP systems.
How ERP functions
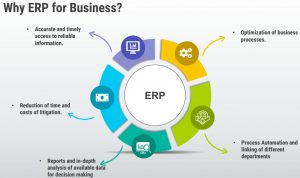
The goal of developing and using ERP Systems is to maximize the capabilities of an organization. It directly increases the efficiency of operations by managing and tracking a company’s resources.
Modular approach enables management of each business operation using a separate module. This is what distinguishes an ERP System from regular business software.
For understanding let us give you an example. Say for example a customer places a refund request at the CRM module of the system. The request will be shared with the inventory management module, where then the management department will contact the customer and have the item shipped back. The inventory module is updated and as soon as the customer is refunded the accounts module subtracts the cost.
All these modules are connected to a central database that records all information and every module accesses it and shares it according to its functionality. This saves you the hassle of having to enter data multiple times on a separate system each time. It enables departments within an organization to collaborate better and in turn decrease data inaccuracy and increase Return of Income (ROI).
This unified collection and usage of data among departments makes it easy to create reports on data at regular intervals. These reports give you an insight into your business performance for that interval so you know how the resources are being spent.
Types of ERP Systems
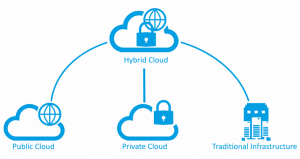
There are three types of ERP systems that are in the market nowadays. We’ll take you through each of them so you know which options are available. The three main types are Hybrid ERP, On-Premise ERP, and Cloud-Based ERP.
On-Premise ERP Systems
These systems are installed locally on a company’s computer or servers. Once implemented, the company has full control over the use and management of the ERP. Typically, to integrate these systems you pay a one time charge. These are easier to modify and customize according to the business’s requirements. But as they say, with great power comes great responsibility.
The business control of the system is in the hand of the organizations. But so is its security as these systems are constantly the target of cyber-crimes. So, organizations have to have a professional team in order to safeguard their data. Another issue faced by these systems is mobility. Mobile accessibility is possible but it again requires a third-party contributor to enable it.
Cloud-Based ERP Systems
Vendors servers host Cloud-Based ERP Systems. Businesses access these servers through web browsers. This is essentially an online system that enabled globalization for ERP Systems worldwide. These systems have monthly/annual pricing plans with additional cost for updates, support, and training. While these solutions are generally less customizable, they offer the benefit of lower hardware costs that otherwise the business could incur. It also takes considerably less time to implement because these are commonly ready-made solutions. As these systems offer very little customizability, vendors release updates very often to cover this shortcoming.
On the other hand, this leaves the system and data security completely in the hands of the vendor. So while making your decision you will have to look up other people’s experiences and understand what measures the vendor takes for security. In addition, the general cost of monthly or annual subscriptions will in time be greater than an initial upfront investment in a customized option.
Hybrid ERP Systems
A combination of the two systems, on-premise, and cloud-based, gives way to a solution that offers the best of both worlds. Not only will this system decrease the amount of money you spend, but it will also offer the reliability an on-premise system can offer. Because these systems combine the ERP abilities of both the on-premise and cloud-based systems, they are called two-tier models.
Businesses that have previously invested a lot in on-premise ERP systems are not willing to completely discard the system. Nowadays, Hybrid ERP Systems are a smarter solution instead of throwing away the system altogether, a reallocation of some features to cloud-based services is much more cost-effective. Some modules are still on-premise while others provide services through the cloud.
These systems lower implementation costs as well as maintenance and training costs. They increase accessibility for your system even when you are offline. When offline, these systems function as on-premise systems and as soon as they have connectivity again, they sync all the data on the cloud.
You should clearly understand the differences between on-premise and cloud-based ERP before making a decision.
Does My Business Need an ERP System?
Whether you’re a small business or a medium-sized company at some point along the way you might need an ERP system integrated into your business model. You as a business owner know that you have to look after both the short term and long-term growth of the company. Chances are that if you’ve come to read this blog you already think you need one. To be absolutely sure you need to ask yourself the following questions.
- Are some business operations constantly reaching a bottleneck? Are they becoming increasingly inefficient?
- Do these inefficient tasks no longer support the growth of your company?
- Do these operations lack security requirements to eliminate risks?
If your answer is yes to even two of these questions, you need to have an ERP system integrated into your business module.
Problems You Might be Facing
These problems are a sign of an unbalanced string of operations that thus cause inefficiency. We are sure that you can identify some of the problems from our list.
- Essential daily tasks like accounting and finance are difficult and time taking. They are either paper-based or are done through separate inefficient software solutions
- Day to Day tasks are increasingly time-consuming and are hard to keep up with
- Managing data through separates databases for each module, resulting in redundant(repetitive) data which is getting increasingly hard to sync with daily
- IT department spends most of their time fixing issues to keep up with the growth of the business
- The current solution has become obsolete and does not support new technological advances like IoT etc.
These are only a few of the major problems we think you might be facing. There are numerous other problems as well. If you’ve found some of the problems, you’re facing above its time to take the next step. You need to have these broken processes fixed and overcome these challenges so you can make room for new growth and a better ROI.
How an ERP System Will Help Your Business
The design of the ERP aligns with the business model of the organization. When integrated properly these systems make room for a lot of business development and new possibilities.
Cost Saving
As a result of the integration of the ERP system a lot of manual, time-consuming tasks are automated and thus save you a lot of money. It frees up employee time and resources.
Reduce Risks
The system is designed to minimize the risks of failure and security. Automation of core business operations leads to less human error.
Scalability
The system needs to be scaled up as well with the growth of your business. When a contract is developed, terms for the growth of the system are set with an agreement between you and the company.
Make Customer and Partner Management Better
Customer relationship management and the supply chain are made better because of different customer modules. Customers receive better responses because of notification systems. ERP systems have helped the Customer Care department a lot.
Improve Business Insight
The collection of data in one place enables the creation of reports for better business insights. Consequently, it helps you make better and informed decisions for your business.
Conclusion
We hope that we were able to help you understand what ERP systems are. This was just an introduction to what these systems are and a guide to help you see what’s going wrong in your business. Once you decide to take a step further and have a system built for your business, we recommend you read up on some of our articles regarding different systems: Health Care, HRM (Human Resource Management), and Retail & Distribution. Whatever queries you may have feel free to leave a comment.